
多线程基础
一、含义
进程
在操作系统中运行的程序就是进程。 例如QQ。播放器,游戏等线程
一个进程里面可以有多个线程。 例如视频里面的,字母,声音等
二、创建线程的方法
继承Thread类
自定义线程类继承Thread类
重写run()方法。
创建线程对象,调用start()方法启动线程。
public class ThreadDemo extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { //重写run方法 for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { System.out.println("我是多线程"+i); } } public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadDemo threadDemo = new ThreadDemo(); threadDemo.run(); for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { System.out.println("我是主方法"+i); } } }线程不一定立即执行,由cpu调度执行
实现Runnable接口
定义类实现Runnable接口
实现run方法,重写方法体
创建线程对象,调用start()方法开启线程
//实现runnable接口创建线程 public class ThreadDemo3 implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { //重写run方法 for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { System.out.println("我是多线程"+i); } } public static void main(String[] args) { //创建线程对象 ThreadDemo3 threadDemo3 = new ThreadDemo3(); //创建threa线程。并开启线程 new Thread(threadDemo3).start(); for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { System.out.println("我是主方法"+i); } } }
实现Connable接口
实现Callable接口,接收返回值类型
重写call方法,处理抛出异常
创建目标对象
创建执行服务
提交执行
获取结果
关闭服务
三、线程停止
线程自己正常停止
设置一个标志位,让线程停止。
package org.example.testdemo.demo1; public class ThreadStop implements Runnable{ private static Boolean flag = true; @Override public void run() { int i = 0; while (flag){ System.out.println("线程正在运行"+i++); } } public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadStop threadStop = new ThreadStop(); new Thread(threadStop).start(); for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { System.out.println("主方法"+i); if (i == 900){ flag = false; System.out.println("线程停止"); } } } }
四、sleep线程休眠
使用线程休眠进行倒计时
使用线程休眠进行获取系统当前时间
//sleep练习模拟倒计时
public class sleepTest {
// public static void main(String[] args) {
// try {
// turnDown();
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// throw new RuntimeException(e);
// }
// }
public static void turnDown() throws InterruptedException {
int num = 10;
while (true){
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(num--);;
if (num<0){
break;
}
}
}
//获取系统当前时间
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Date date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
while (true){
System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss").format(date));
Thread.sleep(1000);
date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
}
五、Join线程强制执行/插队
join方法是合并线程,此线程之行完后再执行其他线程
public class JoinTest implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("线程开始插队");
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println("线程插队"+i);
}
System.out.println("线程结束插队");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
JoinTest joinTest = new JoinTest();
Thread thread = new Thread(joinTest);
thread.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 600; i++) {
System.out.println("主线程正在执行+"+i);
if (i==200){
thread.join();
}
}
}
}
六、state线程状态
线程有五种状态
new 新生 ,runnable 执行, blocked 阻塞, waiting 等待, timed_waiting 等待另外一个线程。terminated 退出
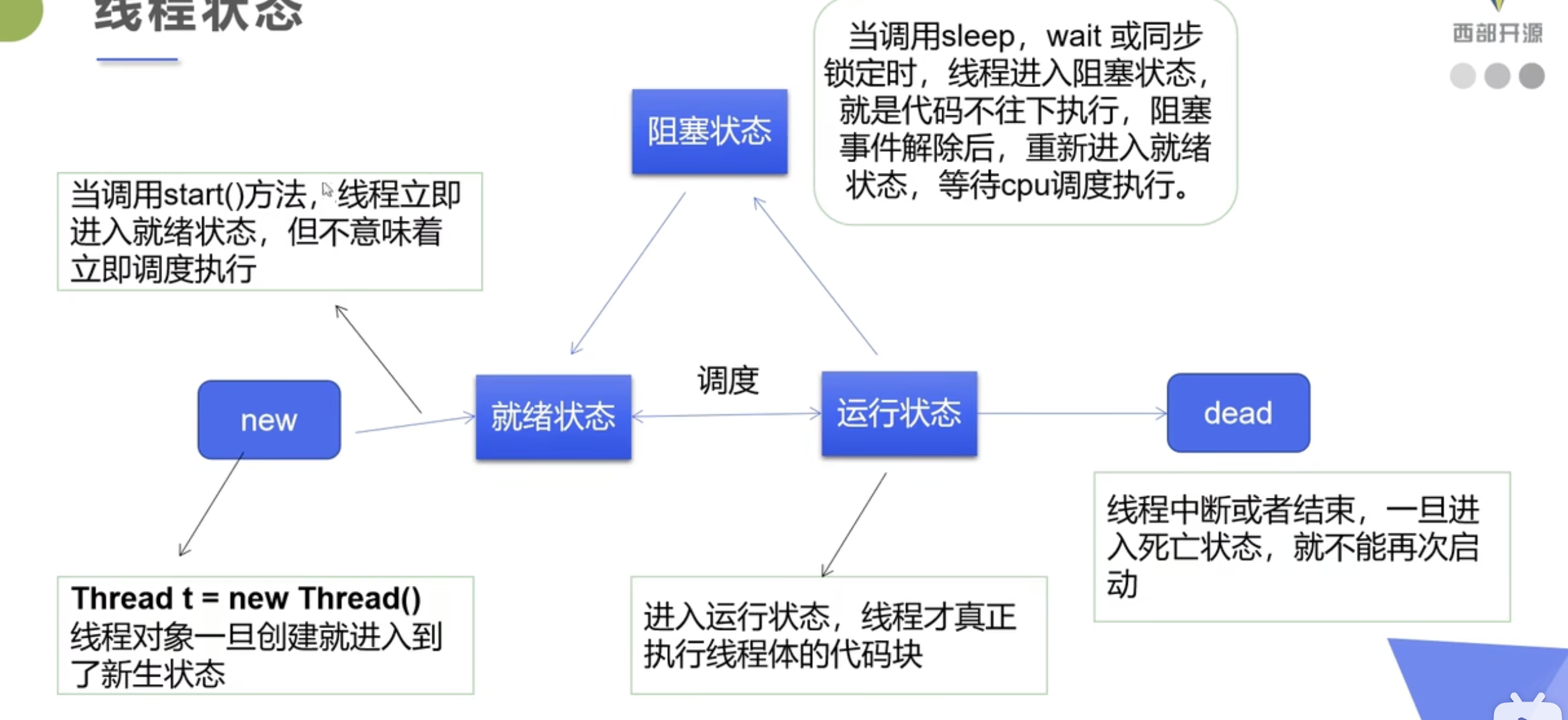
//线程状态
public class StateTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
System.out.println("////////");
});
Thread.State state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
thread.start();
state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
while (state != Thread.State.TERMINATED){
Thread.sleep(100);
System.out.println(state);
state = thread.getState();
}
System.out.println(state);
}
}
七、守护线程
线程分为用户线程(main)和守护线程(后台记录日志,监控内存,垃圾回收)
虚拟机必须确保用户线程执行完毕
虚拟机不用等守护线程执行完毕
public class DaemonTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Shou shou = new Shou();
Thread thread = new Thread(shou);
//设置守护线程
thread.setDaemon(true);
thread.start();
Yong yong = new Yong();
new Thread(yong).start();
}
}
class Shou implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
System.out.println("这是守护线程");
}
}
}
class Yong implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println("这是用户线程");
}
System.out.println("用户线程结束");
}
}八、synchronized同步块
synchronized(obj){}
obj为同步监视器,可以是任何对象。
同步方法中无需制定同步监视器,就是这个对象的本身
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (list){
list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}).start();
}
// Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(list.size());
}九、死锁
多个线程各自占有一些共享资源,并且相互等待其他线程占有资源才能运行。而导致两个或多个线程都在等待对方释放资源,都停止执行的情况。
某一个同步块同时拥有两个以上对象的锁。
产生死锁的必要条件(破坏其中一个就可避免死锁)
互斥条件:一个资源每次只能被一个进程使用
请求与保持条件:一个进程因请求资源而阻塞时,对已获得的资源保持不放
不剥夺条件:进程已获得资源,在未使用完之前,不嫩强行剥夺
循环等待条件:若干进程之间形成一种头尾相接的循环等待资源关系
//死锁模拟练习
public class DelLockTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Eat eat = new Eat(0,"小明");
Eat eat1 = new Eat(1,"小红");
eat.start();
eat1.start();
}
}
class Apple{}
class Banner{}
class Eat extends Thread{
static Apple apple = new Apple();
static Banner banner = new Banner();
int choose;
String name;
Eat(int choose,String name){
this.choose = choose;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
eatFruit();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
private void eatFruit() throws InterruptedException {
if (choose == 0){
synchronized (apple){
System.out.println(this.name+"我想吃苹果");
Thread.sleep(1000);
// synchronized (banner){
// System.out.println(this.name+"我想吃香蕉");
// }
}
synchronized (banner){
System.out.println(this.name+"我想吃香蕉");
}
}else {
synchronized (banner){
System.out.println(this.name+"我想吃香蕉");
Thread.sleep(3000);
// synchronized (apple){
// System.out.println(this.name+"我想吃苹果");
// }
}
synchronized (apple){
System.out.println(this.name+"我想吃苹果");
}
}
}
}十、Lock锁
显式定义同步锁对象来同步,一般使用ReentrantLock对象
lock与synchronized
lock是显式锁(需手动开锁和解锁)synchronized是隐式锁,出了作用域自动释放
lock只有代码锁,synchronized有代码锁和方法锁
lock性能和扩展性比synchronized好
public class LockTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LockTest2 lockTest2 = new LockTest2();
new Thread(lockTest2).start();
new Thread(lockTest2).start();
new Thread(lockTest2).start();
}
}
class LockTest2 implements Runnable{
int ticketNum = 10;
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
try {
//加锁
lock.lock();
if (ticketNum>0){
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(ticketNum--);
}else {
// System.out.println("没有了");
break;
}
}finally {
//解锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}十一、线程通信方法
管程法
package com.example.demo.thread; //测试线程通信,管程法 public class PcTest { public static void main(String[] args) { SynContainer synContainer = new SynContainer(); Product product = new Product(synContainer); Costumer costumer = new Costumer(synContainer); product.start(); costumer.start(); } } class Product extends Thread{ SynContainer synContainer; public Product(SynContainer synContainer){ this.synContainer = synContainer; } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { synContainer.push(new Chicken(i)); System.out.println("生产了"+i+"只鸡"); } } } class Costumer extends Thread{ SynContainer synContainer; public Costumer(SynContainer synContainer){ this.synContainer = synContainer; } @Override public void run() { //消费者消费 for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { System.out.println("消费了第"+synContainer.pop().id+"只鸡"); } } } class Chicken { int id; public Chicken(int id){ this.id = id; } } class SynContainer{ Chicken[] chickens = new Chicken[10]; int count = 0; //生产 public synchronized void push(Chicken chicken){ if(count == chickens.length){ try { this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } chickens[count] = chicken; count++; //唤醒其他线程 this.notifyAll(); } //消费 public synchronized Chicken pop(){ if (count==0){ try { this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } count--; Chicken chicken = chickens[count]; this.notifyAll(); return chicken; } }信号灯法,标志位解决
package com.example.demo.thread; //测试线程通信,标志位 public class PcTest1 { public static void main(String[] args) { Tv tv= new Tv(); new Play(tv).start(); new Watch(tv).start(); } } class Play extends Thread{ Tv tv; Play(Tv tv){ this.tv = tv; } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { this.tv.play("嘻嘻哈哈"); } } } class Watch extends Thread{ Tv tv; Watch(Tv tv){ this.tv = tv; } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { this.tv.watch(); } } } class Tv { String voice; boolean flag =true; //表演 public synchronized void play(String voice){ if (!flag){ try { this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } System.out.println("演员表演了"+voice); this.notifyAll(); this.voice = voice; this.flag = !this.flag; } //观看 public synchronized void watch(){ if (flag){ try { this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } System.out.println("观众观看了"+voice); this.notifyAll();; this.flag = !this.flag; } }
十二、线程池
ExecutorService线程池接口,常见子类:ThreadPoolExecutor
execute方法: 执行任务,无返回值,一般执行Runnable
submit方法:执行任务,有返回值,一般执行Callable
shutdown方法:关闭连接池
Executors:工具类
package com.example.demo.thread;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
//线程池测试类
public class PoolTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 创建线程池
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
//2. 执行线程
executorService.execute(new MyThread());
executorService.execute(new MyThread());
executorService.execute(new MyThread());
executorService.execute(new MyThread());
//3. 关闭线程
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
class MyThread implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
